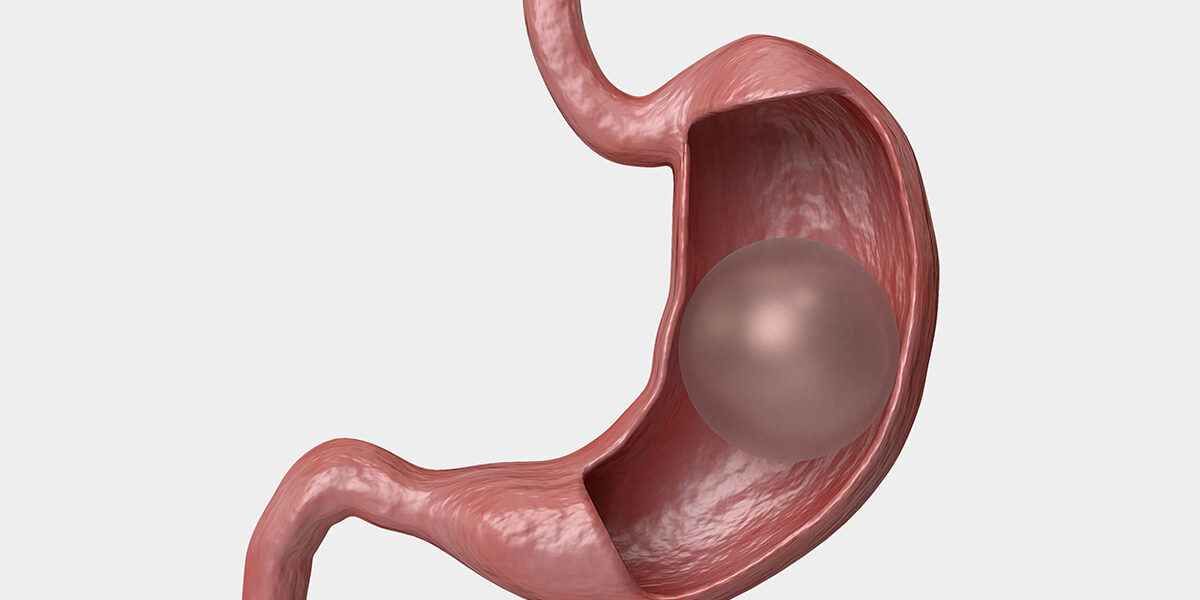
What is Gastric Balloon Placement?
Gastric Balloon : The gastric balloon is made of materials that do not cause any harm to human health. The Gastric Balloon is composed of a deflated balloon that will be placed in the stomach, an 80-85 cm long silicone hose with a diameter of approximately 5 mm and a flexible steel guide wire inside this hose that prevents uncontrolled bending. The gastric balloon is inserted through the mouth into the stomach, with a deflated and vacuumed balloon in the front and a hose behind it. The hose is equipped with distance markings on it, and it is assumed that the balloon reaches the stomach after about 50 cm from the front incisors. Then, with the endoscopy device, the stomach is accessed through the mouth and monitored with the endoscopic camera and it is checked whether the balloon is in the stomach or not. Upon verifying that the balloon has been placed in the proper position in the stomach, the guide wire in the hose to which the balloon is attached is first taken out. Then, 350-500 cc of methyl blue-colored saline is injected through the outer opening of the hose, monitored by an endoscopic camera, to inflate the balloon. Once inflated, the hose is detached from the balloon and taken out, leaving the inflated balloon inside the stomach.
Why is a Gastric Balloon placed?
Gastric Balloon Placement is a procedure aiming to occupy 350-500 cc of the total volume of the stomach, i.e. 1500-2000 cc, with a balloon in order to ensure that the stomach gets full with less food and to create a feeling of satiety. Another advantage of the gastric balloon placement is that it allows the stomach to empty later, as the balloon blocks the gastric outlet like a plug. Longer periods of satiety are achieved as the stomach gets full with less food and takes longer to empty. This helps to ensure that weight loss is achieved by consuming less food. There are two mechanisms involved in the development and maintenance of satiety. The first is a rise in blood sugar, but this has a weak effect. The second is satiety caused by the filling of the stomach and the pressure of the stomach contents on the stomach wall, which is a strong mechanism of satiety. Gastric balloon induces prolonged and potent satiety.
Is it a correct approach to place a Gastric Balloon without any examination to anyone who asks for it and why?
An endoscopic examination of the structure called PYLORUS, which controls the gastric outlet, and which works like a kind of “valve” consisting of a muscular structure and ensures controlled emptying of the stomach, should be performed and the treatment method to be followed should be decided afterwards. During endoscopy, a mild mechanical stimulation is performed with the tip of the endoscope around the PYLORUS. If the pylorus is completely closed upon stimulation, i.e. if it is functional (Normotonic Pylorus), a gastric balloon can be placed without any hesitation and the procedure would definitely result in an effective weight loss.
However, if the Pylorus fails to close completely (Hypotonic Pylorus) or if it does not close at all and is completely open (Atonic Pylorus) upon mechanical stimulation applied to the pyloric region with the tip of the endoscope, the effects of gastric balloon would be limited. The effect of the gastric balloon would be limited to the effect that will result from the fact that the gastric balloon will exert pressure on the gastric outlet and cause the stomach to empty late. In the case of patients with an “atonic” or “hypotonic” pylorus, it is necessary to perform the procedure called “PYLORIC REVISION” first during the same session (You may find further information on Pyloric Revision in the PYLORIC REVISION PROCEDURE under the heading Endoscopic Treatments for Obesity). If gastric balloon is administered in combination with PYLORIC REVISION to those who have HYPOTONIC and ATONIC pylorus, the gastric balloon would again yield an effective weight loss (1).
Does Gastric Balloon Placement require any preliminary preparation?
Yes, it does. If the patient who will undergo the procedure is taking any blood thinners (aspirin, coraspin, coumadin, etc.), he/she should stop taking them 5 days before the procedure. It is important that there are no food residues in the stomach in order to obtain a sufficiently clean image during the procedure, so oral intake of any liquid-solid food and medication should be avoided 12 hours before the procedure.
How long does it take to place a Gastric Balloon?
All the procedures (including mild narcosis) involved in Gastric Balloon Placement are completed in about 10-15 minutes. The patient is discharged after 2 hours. In the next 2 hours, the patient can start eating and resume his/her daily life.
How do I prepare for the procedure in the hospital, do i feel anything during the procedure?
Following the necessary preliminary preparations of the patient, a vascular access is established following fasting for 12 hours, then the patient is slightly anesthetized under the supervision of an anesthesiologist in the standard endoscopy ward in the hospital, and while the patient is asleep with normal breathing and without feeling anything, the endoscopy device is inserted through the mouth to reach the stomach, and at that point, a preliminary examination is performed and if there is no medical drawback, the endoscopy device is removed. First, the balloon is inserted through the mouth and lowered into the stomach. Then the endoscope is inserted through the mouth again and advanced to the stomach. If there are no medical drawbacks, the guidewire is first taken out under surveillance of the camera, and then the gastric balloon is inflated with blue saline, taking into account the volume of the stomach. The patient absolutely feels neither pain nor anything else during the procedure.
For whom can the procedure be postponed as a result of endoscopic examination?
If the endoscopic examination reveals active bleeding, active infection, suspicious mass lesion or obvious tumoral formation in the stomach, the procedure is postponed. In case of suspicious or obvious tumoral formation, a biopsy is conducted. And gastric balloon placement procedure is not performed.
How soon after the Gastric Balloon is inserted should it be removed?
There are two types of gastric balloons. The first is a six-month gastric balloon, which is removed after this period. The other is a 12-month gastric balloon, which is removed after 12 months. However, no side effects appear if it stays 50% longer than the specified time.
Can a new gastric balloon be inserted after the gastric balloon is removed?
If desired, a new balloon can be inserted during the same session after the gastric balloon is removed. There is no need to wait for this procedure. Gastric balloon can be inserted repeatedly, there are no medical drawbacks.
How is gastric balloon removed?
First the patient is made ready for the procedure by following the same steps as during gastric balloon insertion. Following 12 hours of fasting, the patient is put to sleep with sedation (mild anesthesia) given intravenously under the supervision of an anesthesiologist, and the stomach is accessed with an endoscope through the mouth. Through canals in the endoscopy device, a tube is sent into the stomach, which contains a piercing wire that can be removed in a controlled manner. These are controlled externally with endoscopic visualization. At this point, first the site where the balloon will be punctured is identified, then the tube inserted into the stomach through the endoscopy cannula is brought closer to the balloon, followed by opening the piercing wire in the tube, piercing the balloon and penetrating into the balloon. Then, while the tube is still inside the balloon, the piercing wire inside the tube is pulled out and removed. Meanwhile, the inner end of the tube is inside the balloon and the outer end is outside. Using a suction device called an aspirator connected to the outer end of the tube, the liquid in the balloon is drained. As soon as the liquid is completely drained from the balloon, the tube is pulled out of the endoscopic canal. Then, a cannula with two retaining apparatus at the tip is inserted into the stomach through the same canal. The grasping hooks are normally kept closed and can be opened with the camera at any time. The grasping cannula is opened in the stomach in a controlled manner and the emptied balloon is grasped by the grasping hooks of the cannula and the balloon is pulled out of the mouth using the endoscope.
Please contact us for further information about endoscopic treatments for obesity and gastric balloon prices.
References:
- Kanlioz M, Ekici U, Tatli F, Karatas T. Efficacy of Intragastric Balloon Placement and Botulinum Toxin Injection in Bariatric Endoscopy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2020 Dec;30(6):500-503. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000829.
Please contact us to get more detailed information about endoscopic treatments and flora transplantation for obesity. You can reach us via E-mail or Whatsapp.
Before & After





Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A gastric balloon is removed in approximately 10-15 minutes (including mild anesthesia).
Some gastric balloons allow for increasing the volume of the balloon by accessing the stomach through an endoscope and filling it with more fluid or reducing the volume of the balloon by draining some of the filled fluid.
Patients may sometimes have complaints of too much pressure and compression from the balloon, which they cannot tolerate despite adjuvant therapies. In such cases, if the balloon placed is adjustable, the balloon volume can be reduced by endoscopy under anesthesia using a tube inserted into the balloon valve. In some cases, however, if the expected weight loss is not achieved and the patient has no complaints, the volume of the balloon is increased slightly to increase the balloon’s effectiveness.
Those who will undergo gastric balloon placement lose an average of 16-18% weight in a 6-month period, provided that they also follow their diet.
If the gastric balloon application is performed by experienced specialists, the risk it poses is the same as the risk of endoscopy.
While placing the gastric balloon, the volume of the balloon is adjusted taking into account the anatomical structure and volume of the stomach. A gastric balloon inflated too much may cause severe feeling of fullness, pressure, nausea and vomiting. However, 10-15% of patients may experience a feeling of fullness, nausea and vomiting even if the balloon is inflated to the appropriate volume. Most of the symptoms in these cases are alleviated by simple medical treatments. The symptoms usually resolve spontaneously after the first 24 hours however 1-2% of patients may continue to have symptoms after 24 hours. In 0.5-1% of patients, the balloons are removed in the first week following the procedure for not tolerating the balloon.
Theoretically, yes, the gastric balloon can burst. But this is very rarely the case. However, there are cases of balloon bursting reported in populations that habitually eat fish and chicken with bones.
The balloon is inflated with saline colored with methylene blue. If the balloon bursts, the urine color will be green due to the absorption of methyl blue into the bloodstream. Each patient is informed after the procedure that the balloon may have burst if they pass green urine. In such a case, the balloon is checked by endoscopic examination, and is removed if it has burst.
Even if it has burst, it is very difficult for the balloon to pass from the stomach to the small intestine. However, there are some published cases, albeit rare, of a burst balloon passing from the stomach to the small intestine and causing obstruction, and sometimes bursting and being excreted in the feces without being noticed.
