WHAT IS CROHN’S DISEASE?
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
HOW IS IT DIAGNOSED?
HOW IS IT TREATED?
The disease, in its current sense, was first described in 1932 by American “Dr. It was named CROHN’S DISEASE because it was defined by Bernard Burrill CROHN and introduced into the medical literature.
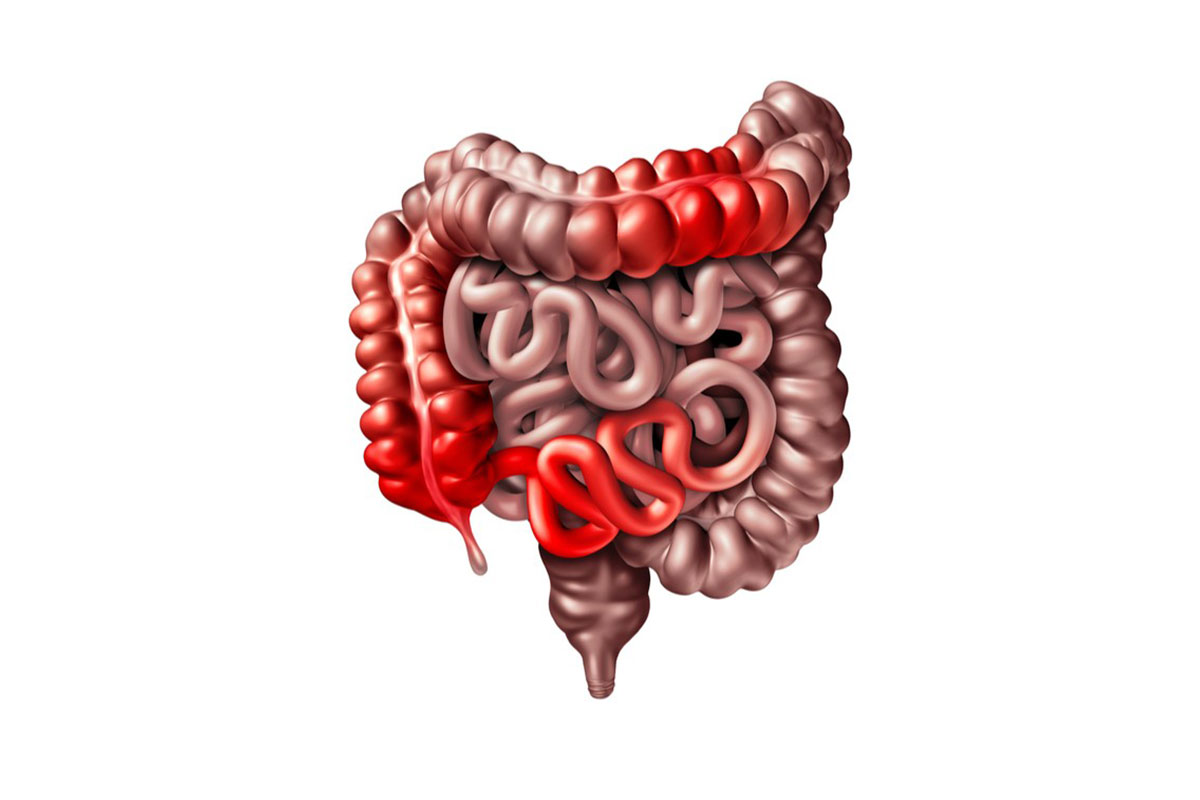
CROHN’S DISEASE is a disease considered in the inflammatory bowel diseases group. This inflammation is an AUTOIMMUNE reaction, where our defense system perceives the body’s own tissues as foreign-harmful and attacks them. IN CROHN’S DISEASE, regional thickening and narrowing occur in the areas involved with the involvement of the inner surface of the digestive system, sometimes ulceration (wound) and granuloma (mass) may also be added to these. Involvements are skip areas and tend to involve more than one area, and these affected areas can vary from a few centimeters to a meter. In CROHN’S DISEASE, involvements can occur in every region from the mouth to the anus, but they are mostly observed in the last parts of the small intestines (distal ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon) (cecum), and this region is called the ileocecal region. Along with thickening and stenosis due to inflammation in the involved area, swelling due to inflammation may also be observed in the regional LYMPH NODES.
CROHN’S DISEASE mostly occurs between the ages of 35-40. There is no obvious gender difference. However, it can also be encountered in earlier and later periods. In the medical literature, it is evaluated in the IDIOPATHIC disease group (cause unknown). However, in CROHN’S DISEASE, family accumulation, that is, genetics, is an important factor. There is a consensus that hereditary and environmental factors play a role in CROHN’S DISEASE. In addition, although the disease is often observed after a triggering traumatic process (severe infection, severe depression, cancer treatment, chemotherapy, etc.), it can sometimes occur even when there is no obvious reason.
CROHN’S DISEASE progresses with recovery (remission) and exacerbations (active disease). Providing long remission is extremely vital in the treatment of CROHN’S DISEASE. Because in each exacerbation period, the thickening and narrowing in the previous affected areas increases, and more importantly, new areas of involvement are formed.
In CROHN’S DISEASE, complete or near-complete obstruction in the intestines may be observed due to stenosis in the affected area. In this case, the only treatment is to surgically remove the narrowed area and restore intestinal fluidity. Due to the stenosis in the retained intestinal segment and the complication we call FISTULA (tunnel), there may be problems between the intestines (entero-enteral fistula), between the intestine and the anus (perianal fistula), between the intestine and the abdominal wall (entero-cutaneous fistula), between the intestine and the vagina (entero-vaginal fistula). etc. may develop. Due to this fistula, the intestine flows into the area where the fistula opens through a tube and causes complications. FISTULA cases in CROHN’S DISEASE are extremely resistant to treatment and tend to fistulize again from the same place or another place after treatment.
Another possible complication in CROHN’S DISEASE is FISSURE (crack) around the anus and ANAL ABSCESS. Fissure and anal abscess, just like fistula, are extremely resistant to treatment and their recurrence rate is extremely high.
WHAT FINDINGS SHOULD WE SUSPECT CROHN’S DISEASE?
- Long-standing abdominal pain, intestinal irritability and nausea
- FIRE that has not decreased for a long time and whose reason cannot be explained
- Persistent oral sores
- BLOOD in the stool
- MUCUS (slimy) appearance in the stool
- Resistant DIARRHEA
- Sometimes constipation in older ages
- Feeling of frequent defecation (tenesmus) and feeling of incomplete evacuation after defecation
- Anemia
- chronic fatigue
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Resistant anal fissure (anal fissure)
- Anal fistula (discharge of feces and/or gas from the side passage other than the anus)
- Anal abscess (anal abscess)
- Those who have had other autoimmune diseases in the past have these findings
HOW IS CROHN’S DISEASE DIAGNOSED?
The patient’s complaints should be listened to very carefully by a physician experienced in his field. The detailed questioning that follows is extremely valuable for diagnosis. With the physical examination, it is evaluated whether there are wounds in the mouth, anal fissure, anal fistula, anal abscess, any skin lesions, nail and skin findings, anemia, swelling in the regional lymph nodes, abdominal tenderness, etc. Then blood tests are performed to monitor the AUTOIMMUNE reaction, blood table and other parameters. Endoscopy and colonoscopy are extremely valuable in diagnosis and are the most important in making the diagnosis. In the endoscopic-colonoscopic examination, finding regional stenosis, tissue thickening, and occasionally ulceration and granuloma formations are specific findings for diagnosis. In addition, BIOPSY (small sample taking) from the areas where findings are detected allows the diagnosis to be confirmed. Contrast-enhanced MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is important in making the diagnosis and especially in identifying fistulas.
HOW IS CROHN’S DISEASE TREATED?
In CROHN’S DISEASE, treatment is evaluated in two parts: suppression of inflammation during exacerbation periods and treatment of complications (intestinal obstruction, fistula, fissure, abscess, etc.).
Many immunosuppressive drugs are used to suppress the AUTOIMMUNE reaction during the exacerbation (attack) period. While these drugs suppress the autoimmune reaction, they also cause irreversible damage to the FLORA structure of the digestive system.
The only treatment for FISTULA, FISSURE, ANAL ABSCESS AND INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION, which are complications of CROHN’S DISEASE, is SURGERY.
The most important and critical thing in CROHN’S DISEASE is to diagnose the disease early and start treatment as soon as possible. The longer and more severely people suffer from the disease, the more irreversible complications occur.
For these reasons, providing the longest possible REMISSION (well-being, disease-free period) periods and the least EXCREASE (attack) periods constitute the basis of the treatment. Because each attack means new areas of involvement and increased complications of existing areas.
Due to the current treatment methods and the medications given to suppress the disease, our digestive system FLORA is further damaged. All research shows that the weakening of the digestive system flora is an important triggering factor in the emergence of CROHN’S DISEASE. OUR FLORA, which has been weakened by suppression treatments, suffers further damage (its biodiversity decreases and sometimes disappears partially or completely), resulting in a vicious circle.
Disruption of the DIGESTIVE SYSTEM FLORA and decrease in biodiversity disrupts the selective permeability of the digestive system and causes LEAKY GUT SYNDROME. Leaky Gut Syndrome is one of the most important factors for the onset of AUTOIMMUNISM. The occurrence of any autoimmune disease accelerates and facilitates the occurrence of other autoimmune diseases. CROHN’S DISEASE is also an autoimmune disease.
According to the examinations, if the damage to the digestive system flora is treated with TOTAL GASTROINTESTINAL FLORA TRANSPLANT from a healthy donor and healthy flora with high biodiversity is introduced, TRAYY GUT SYNDROME can be treated.
Clinical research shows that patients diagnosed with CROHN’S DISEASE often have moderate to severe damage to their digestive system flora. TOTAL GASTROINTESTINAL FLORA TRANSPLANTATION performed on these patients provides serious remission (improvement) and long remission periods. Therefore, complications arising from CROHN’S DISEASE (intestinal obstruction, fistula, fissure, abscess, etc.) are reduced in patients with fewer attacks.
Another currently popular treatment for CROHN’S DISEASE is the method known as GAITA TRANSPLANTATION or FECAL MICROBIAL TRANSPLANTATION (FMT). Stool (stool) taken from a healthy donor and subjected to certain procedures is colonoscopically transplanted to the large intestine of the patient. FMT procedure is also an effective method in the treatment of CROHN’S DISEASE. However, TOTAL GASTROINTESTINAL FLORA TRANSPLANTATION is the GOLD STANDARD treatment for Crohn’s Disease.